Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision. Cruise missiles of today are even capable of travelling at supersonic or high subsonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory. Out of all the cruise missiles in the world, today we would like to pick the 10 best of them all. Enjoy watching. Cheers!
What is a cruise missile?
Cruise missiles, although similar to ballistic missiles in some regards, provide an alternate means to deliver a lethal payload rapidly and accurately to a target. Cruise missiles differ from ballistic missiles in that they fly towards their target at lower altitudes, remaining within the Earth’s atmosphere throughout their trajectory. Cruise missiles are defined as “an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target.” Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned control-guided helicopters or aircraft can be included in this definition, but will not be discussed on this page.
The cruise missile has its beginnings in World War I, when the U.S. Army developed the Kettering Bug, an unmanned aerial bomb designed to strike targets beyond the range of artillery and too dangerous for piloted aircraft. However, the Kettering Bug was never used in combat. Instead, the modern cruise missile originates more from the V-1 Flying Bomb used by the Germany in the last months of World War II.
Launch Platforms
Cruise missiles are capable of being launched from multiple ground, air, sea and submarine platforms. Both fighter and long-range bomber aircraft are capable of carrying and launching cruise missiles. On the ground, cruise missiles are most commonly launched by road-mobile systems due to the inherent advantages of mobility, but they can also be launched from fixed platforms.

Russian warships in the Caspian Sea launch Kalibr cruise missiles towards targets inside Syria.
At sea, various surface ships and submarines can launch cruise missiles. Submarines are capable of launching while surfaced or submerged using torpedo fixtures or vertical launch tubes. In April 2010 Kontsern-Morinformsistema-Agat, a Russian company, began marketing a version of the Russian Kalibr cruise missile housed in and capable of being launched from a standard shipping container.This would allow any vehicle capable of carrying a standard shipping container to become a discreet platform from which to launch cruise missiles.
Propulsion and Flight
Cruise missiles utilize jet engines as their primary method of propulsion. Most cruise missiles are subsonic and use Turbofan and Turbojet engines. While less common, supersonic and hypersonic cruise missiles utilize Ramjet and Scramjet engines. Some also use rocket motor propulsion as a booster in the first phase of flight or to accelerate to supersonic speeds in the terminal phase.
Cruise missiles can fly to their targets at varying altitudes as long as they remain within the atmosphere. The trajectory of most remains close to the Earth’s surface, sometimes skimming just meters above the ground. Their low flight path makes it much harder for most radar and sensor systems to detect the missile, unless the radar or sensor system is airborne and directed towards the ground. Some cruise missiles will fly only at high altitudes and dive sharply down once they reach their target. Flying at high altitude can extend the range of the missile because it’s more fuel-efficient than flying at lower altitudes. However, this also makes the missile more susceptible to missile defense systems since today’s radars and sensors are typically positioned to detect and track high altitude threats. Cruise missiles can also mix their flight trajectory between high and low altitude in order to get the benefits of both. In this instance, cruise missiles will typically fly at a high altitude early in their flight to help extend their range, but as they approach their target, or missile defenses, they will fly down to a lower sea skimming/terrain hugging altitude to help it evade detection and defenses.
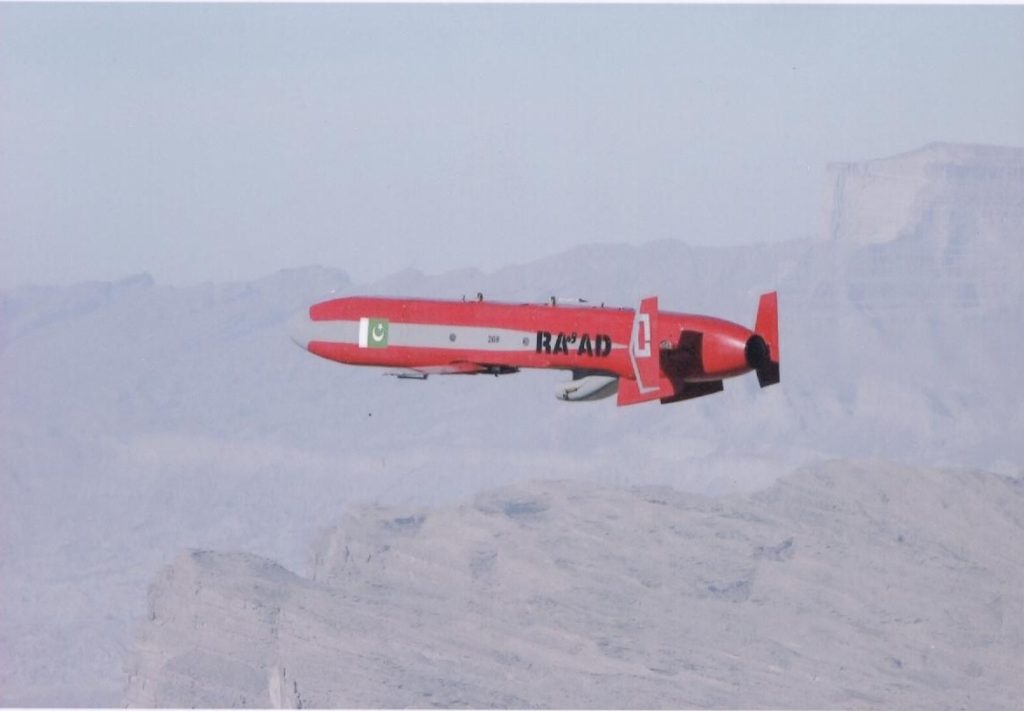

Flight test of Pakistan’s Ra’ad cruise missile.
Guidance
Cruise missiles can use multiple guidance methods in order to accurately place their ordinance on the desired target and avoid missile defense systems. One of the first methods used by cruise missiles was inertial guidance, which is still used today and allows the missile to fly along a flight path programmed prior to launch. Another guidance method is terrain contour matching (TERCOM), which compares a terrain map to the current terrain the missile is flying over to ensure the missile is flying on the correct path. Some use GPS systems, which require connection to either GPS or GLONASS satellite system, but can help ensure the missile follows the correct flight path and strikes the final target using specific coordinates with a high degree of accuracy.
Other guidance methods are primarily used in the terminal phase of flight to increase accuracy. One is a laser guided system which uses a sensor to detect its target painted by a laser, however this can be unreliable because dust and smoke can interfere with the laser or the missile may not always be able to see the laser or painted target. Another terminal guidance method is TV guidance, in which an operator uses a camera in the nose of the missile to visually identify and manually guide the missile to the target in its final phase. This method also gives the operator the option to abort the strike in the final phase if an anomaly is detected. A radar seeker is also used in the nose of some missiles to identify and/or keep the missile on target in the terminal phase. These radar seekers use either passive radar, which detect radar emissions of their target, or active radar, which emit their own radar to detect their target. Infrared (IR) guidance – directing the missile towards heat emitting objects, such as engines – may also be used by cruise missiles in the terminal phase. However, because of its simplicity, IR guidance cannot differentiate between friendly, adversarial, or extraneous IR signals in a crowded battlefield, and is usually used in conjunction with other guidance systems. The last guidance system used by cruise missiles is Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC), which uses a camera in the missile to find the desired target and match it to a stored image using an image correlator.
Payload
Cruise missiles are typically armed with conventional or nuclear warheads, but can also be equipped with chemical or biological warheads. The warhead weight and yield can vary widely, depending on the specific cruise missile and its mission.