An airforce is a crucial part of any army – air superiority provides cover and safety for the troops on the ground. More importantly, fighter jets help protect bombers, so superior fighter jets are a must for every country that wants to secure their positions as a prominent military force in the world.
Currently, fifth-generation jet fighters are the most advanced fighter jets. American military aircraft builder Lockheed Martin defines fifth-generation fighters having these characteristics:
- All-aspect stealth when armed;
- Low-probability-of-intercept-radar, meaning it can avoid radar detection;
- High-performance airframes;
- Advanced avionics;
- Highly integrated computer systems capable of connecting to other systems for situational awareness.
With this in mind, let us count down the top 10 most advanced jet fighter in 2019!
10. Dassault Rafale
The fighter jet developed by the French company Dassault is a multirole fighter.
As the French Air Force were sought after new aircraft to replace its current fleet, France, in order to reduce costs agreed to enter into an agreement with other European countries. As disagreements arose, France decided to develop its own fighter – the Rafale. The fighter jet first entered service in 2001 and ever since has been regarded as one of the best military aircraft in the world.
9. McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle
Developed by McDonnell Douglas and later on by Boeing, the F-15 is still produced. But, Boeing is set to end the production of F-15 in 2022. Even though it was delivered more than 35 years ago, the F-15 is still considered a very capable fighter in the air. It still is operated by 4 countries: Israel, Japan, Saudi Arabia, and the United States.
Recently, an F-15 has hit headlines as an Israeli F-15 lost a canopy at 30.000 feet in the air.

F-15 Eagle Fighter Jet
8. JF-17 Thunder
The JF-17 Thunder or the FC-1 Xiaolong is a multirole combat aircraft. Developed by a joint-operation between China and Pakistan to provide the Pakistani Air Force with a cheap and modern alternative to its aging and a large fleet of various fighters, bombers and interceptors. Because of this, the JF-17 is going to become the backbone of the PAF.
After a difficult time of testing and redesigning, PAF finally received its first jets in 2007. Ever since then, the Pakistani Air Force has heavily relied on the JF-17 to conclude various missions in its territory. In 2013, PAC Kamra began the production of the Block 2 JF-17 – the updated jet has air-to-air refueling, better avionics, better load capacity, data link and electronic warfare capabilities.
8. HAL Tejas Fighter Jet
The HAL Tejas is an Indian fighter jet that is replacing the MiG-21, which the Indian Air Force has been using since 1964. Pilots praise the HAL Tejas for its high maneuverability. Production on the fourth-generation Indian jet fighter began recently, due to the fact that the program struggled to obtain an Operational Clearance.
 HAL Tejas
HAL Tejas
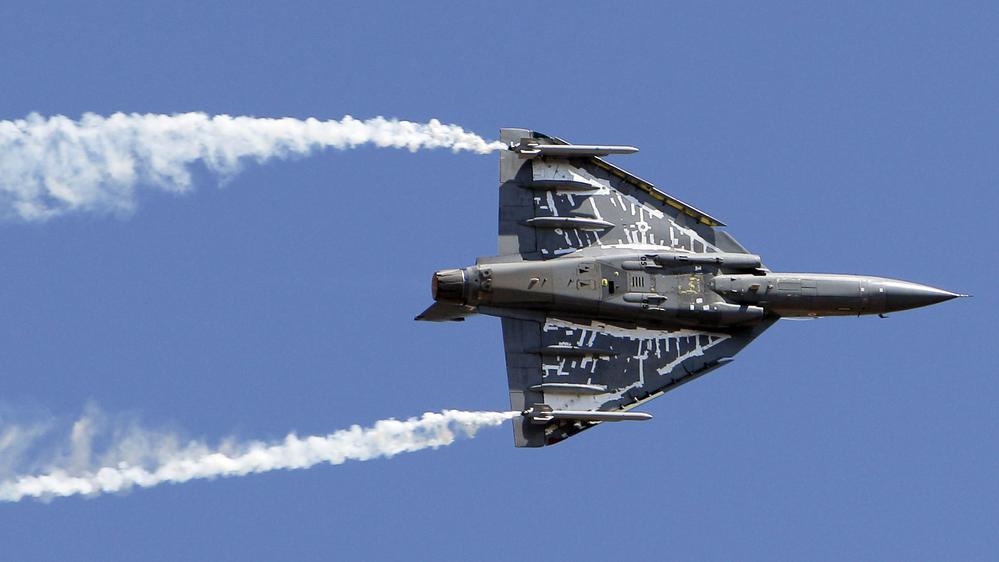
7. Eurofighter Typhoon
Out of all the fighter jets in the list, the story of the Typhoon is one of the most interesting ones. A joint operation of Airbus, BAE Systems and Leonardo, an Italian company developed the Typhoon. After development began in 1983, the first official test flight took off in 1994. The Typhoon was plagued by delays. After the fall of the Berlin Wall and a change of government in Germany, the Chancellor of Germany at the time made a promise to cancel the project. However, the program survived and after a myriad of delays Germany deployed the first Eurofighter Typhoons.
6. Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor
The first fifth-generation fighter jet in the world, the F-22 Raptor entered service in 2005. The United States government canceled the Raptor in 2011. Even though it was a critical part of the USAF (the United States Air Force), the rising development and maintenance costs, lack of air-to-air missions put an end to the production of the jet. Lockheed delivered the last Raptor to the USAF in 2012.
Nevertheless, the F-22 was a pioneer. It was the first fighter jet to combine supercruise, supermaneuverability, stealth and sensor fusion.
5. Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin
A unique example on the list, the Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin is a fifth-generation… test aircraft? Yep. Even though it’s not a fighter jet in itself, the Japanese are using the X-2 as a testbed for other fighter jet technologies. The backstory of this jet is that Japan was looking to replace its fleet of current fighters. The Japanese government contacted the United States for the possibility of purchasing F-22 Raptors, but the U.S. Congress shot down any probability of that happening to protect its military secrets.
The first Shinshin flight took off in 2016 and after successful tests, Mitsubishi started producing the aircraft. The X-2 is a predecessor to the F-3, a sixth-generation fighter jet. The Japanese are going to produce the F-3 from 2027.
 Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin
Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin
4. Shenyang FC-31
FC-31 or the J-31 is the second fifth-generation fighter jet that is going to be introduced into the Chinese Air Force. Although less advanced than its counterpart, the Chengdu J-20, it is still a very capable fighter jet. The exact specifications remain unclear for anyone that is outside the Chinese Military. Foreign experts, primarily US ones, indicate that the FC-31 is on par with other fifth-generation fighters. However, the better jet is decided by a multitude of other factors. Namely, the readiness of the pilots and capabilities of radars and sensors of the aircraft.
 Shenyang FC-31
Shenyang FC-31
3. Chengdu J-20
The best Chinese fighter jet, the Chengdu Aerospace Corporation introduced the J-20 in 2017. After more than 20 years of development, it first flew in 2011. There were quite a few changes to the design of the aircraft after the first flights took place, namely a new intake, new stealth coating and a new design of the vertical stabilizers. In spite of some issues that arose after production, the Chengdu J-20 is the first fifth-generation fighter jet in Asia.
 Chengdu J-20
Chengdu J-20
2. Sukhoi Su-57
Developed by Sukhoi Company, the Su-57 is going to become the most technologically advanced Russian fighter jet. It’s the first fighter to tick every box in the list of fifth-generation fighter features. Sergey Bogdan was the first pilot to test the Su-57 in 2010. Compared to the F-35, the Su-57 only cost the Russians an estimated $10 million to research, develop and prepare for production.
The Russian Air Force is expected to introduce them into full service in 2019. However, in 2018, journalists spotted two Su-57s in Syria.
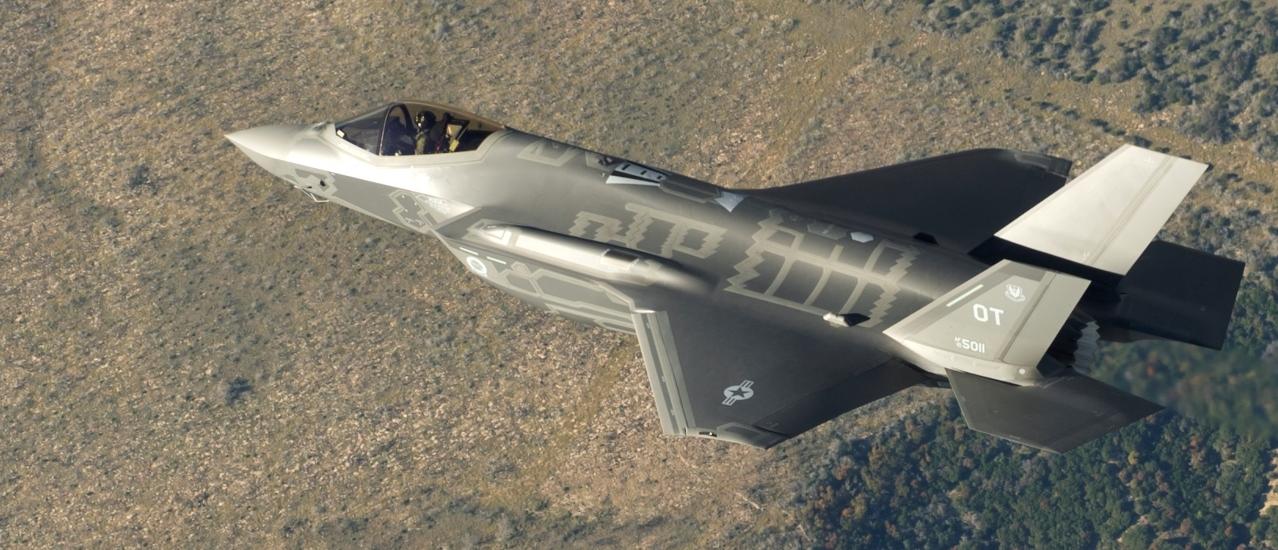
1. Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II
United States Air Force introduced the newest fighter jet in 2015. The F-35 has three main variants, with differences in their landing capabilities. The estimated cost of the F-35 program is mind-blowing. The US government spent a whopping $1.508 trillion on the fighter jet. But on the other hand, Lockheed projects that the USAF will utilize the fighter jet until 2070. Although the F-35 has its critics, it certainly cannot be denied that it is the most advanced fighter jet currently in the air.













 HAL Tejas
HAL Tejas Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin
Mitsubishi X-2 Shinshin Shenyang FC-31
Shenyang FC-31 Chengdu J-20
Chengdu J-20
